Public and private keys are essential to cryptocurrencies, representing a fundamental part of their functionality within the public-key cryptography (PKC) framework. With the help of these keys, you can carry out crypto transactions on your own without the assistance of a third party.
Together, these keys form a key pair, allowing you to receive cryptocurrency from anyone, anywhere, and at any time using your public key. Most importantly, you must always keep private keys private and take precautions to secure them. If your private keys get into the wrong hands, they can enable unlawful access to any crypto associated with them.
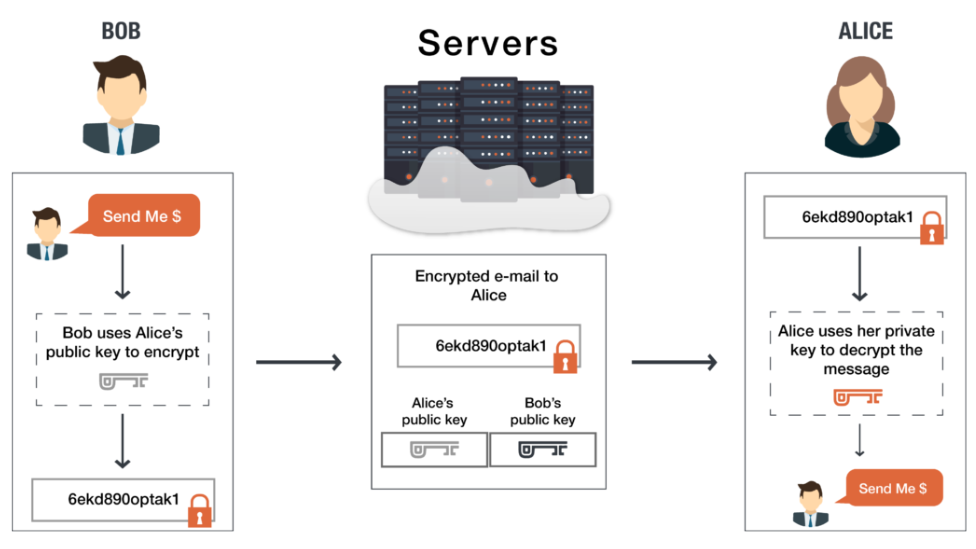
What Is Public-Key Cryptography?
PKC is a technology that is essential in ensuring the validity of data authenticity through asymmetric encryption. PKC was initially used primarily for message encryption and decryption in traditional computing. But when it comes to cryptocurrency, PKC has become crucial for safeguarding and validating transactions. Without PKC, cryptocurrency as we know it would be virtually impossible to implement.
PKC operates on “trapdoor functions,” or one-way mathematical functions. These functions are made to be simple to solve in one direction but are exceedingly difficult, if not downright impossible, to reverse engineer. Reverse engineering these functions would require a supercomputer’s computing capacity and thousands of years to complete.
What Is a Private Key?
A private key allows users to prove ownership and spend funds connected with their public address. Generally, a private key can take several different forms. These include 256-character long binary codes, 64-digit hexadecimal codes, QR codes, or Mnemonic phrases.
Where Are My “Private Keys?”
Private keys are kept in a crypto wallet, which can be either mobile or desktop software or a specific hardware device. The crypto blockchain network does not contain your private keys. If you store digital currency on an exchange, the exchange becomes the custodian of your private keys. This means you entrust it with your keys like you would entrust a bank’s vault with your gold.
Nonetheless, you have control of your keys if you move your crypto from an exchange to a non-custodial wallet. Because of the configuration and function of cryptocurrency wallets, you will rarely have to deal with private keys directly because wallets manage them automatically. As a backup, users usually get a seed phrase that encodes their private keys.
Managing Cryptocurrency: Understanding the Role of Public and Private Keys
In order to understand how crypto transfers work, you need to know how public and private keys work together. Basically, when you say you have cryptocurrency, you really mean that you have a private key proving you own it. It’s on the blockchain, so anyone can access your public key to demonstrate that you are the owner.
Takeaways
Understanding how public and private keys work is a vital part of any crypto investment efforts. Users need to manage public-private key pairs and the PKI with the utmost care because of their significance in protecting important data.