Every growth-oriented economy recognizes the importance of agriculture and technology in sustenance. Although the agricultural sector is established, the use of blockchain technology can aid in transforming the industry.
Why blockchain is necessary for the agricultural sector
In one phrase, agriculture is indispensable. The World Bank has established a working food system’s importance in achieving developmental goals. A growing agricultural sector is a powerful tool for ending extreme poverty and raising income two to four times more than other sectors.
However, all across the globe, the agricultural market is facing a crisis. Rising food insecurity and climate change are some of the major factors that threaten this sector. Its instability has led to food waste, malnutrition, and increasing hunger.
The revolutionary nature of blockchain can be of particular benefit to the agricultural sector. Blockchain technology can meet consumer demands and transform agricultural commerce through decentralized and transparent processes.
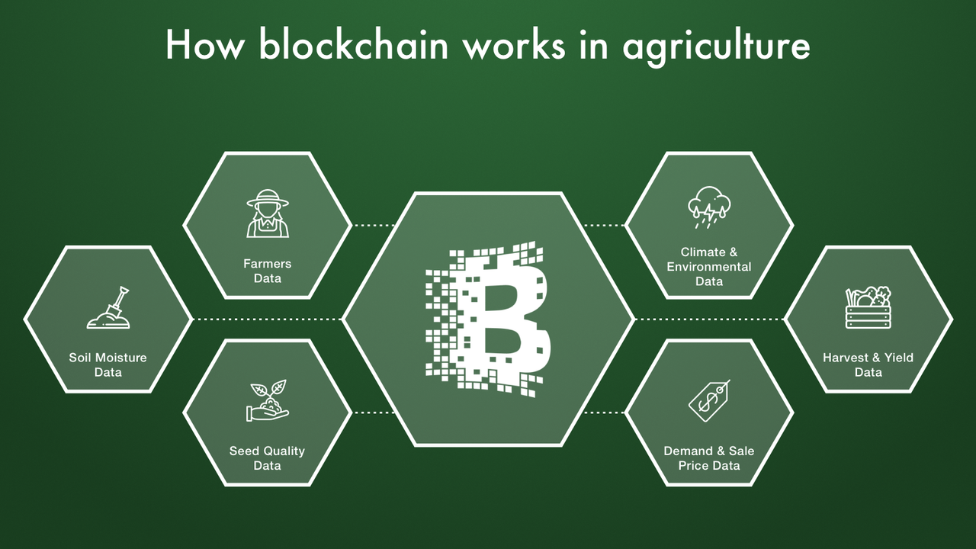
How blockchain can transform the agricultural sector in the Middle East
Blockchain can transform agriculture through the following mediums
- Food supply chain
The immutable nature of blockchain makes it easy for consumers to trace the origins of every food product purchased. In this way, consumers can be reassured of the safety of farm products. Similarly, farmers benefit from blockchain when they are kept abreast of the demand and supply chain. Farmers can optimize their prices, and consumers can hold them accountable for the quantity and quality of their products.
- Farm management
When farm processes and services are automated through blockchain, it reduces the occurrence of human errors. Through artificial intelligence, farmers can understand the quality of seeds, crop type, and possible diseases to attack the crops. Subsequently, food wastage, crop spoilage, and misuse of resources are reduced.
- Food payment options
Traditional payment options require intermediaries, which is often costly and takes longer. With blockchain, farmers and consumers can negotiate directly and agree on a reasonable price for goods. Parties can also utilize smart contracts that automatically trigger payment when certain conditions are met. In addition, blockchain opens new markets to farmers and allows consumers to access farm produce beyond geographical borders.
- Food security
There is usually no food security because farmers cannot monitor weather conditions that can damage their crops. By using blockchain, farmers can be alerted to the change in climate and take preventive actions. Ultimately, food security will no longer be an issue, as the appropriate measures are taken long before any catastrophe.
- Farm financing
A booming agriculture sector requires substantial financing. Although traditional systems provide loan services for farmers, it is constrained by long processes. Blockchain gives both limited and large-scale farmers access to financial services. The financing provided assists in maintaining and running the farm longer, leading to greater yields
Looking ahead
In the same way, blockchain has the potential to better the processes in several sectors; the agricultural industry is not exempted. Blockchain can transform agriculture as global blockchain in the agriculture market is expected to reach $886.16 million by 2025.
However, blockchain may not transform the agricultural sector if small farmers and rural people are omitted. These issues, including scalability and regulatory frameworks, must be addressed before blockchain fully integrates into the agricultural sector.